Dairy Industry is growing fast using the modern biotechnological techniques and tactis. In manufacture of dairy products, biotechnology has been used for many centuries (cultured milk products, cheeses, processed milk by products) either using starter cultures or enzymes for milk clotting, cheese ripening acceleration, fat, protein or lactose hydrolyzate production or antimicrobial purposes.
Dairy products are recognized as healthy natural products. Modern developments in the biotechnology have opened up new and stimulating possibilities in dairying for enabling the accessibility of milk and milk products within the attain of poor and cater to the needs of large population. Dairy industry, in particular, can enormously promote through biotechnological inventions which can not only develop the overall quality and safety of processed dairy foods but also improve their commercial values for local consumptions and exports. Since, the significant commitment of dairy industry is to offer top notch nutritious, refreshing and cheap dairy nourishments to the shoppers; it has gotten unsurprising to join biotechnological mediation at an alternate phase of milk generation and preparing.
Modern Recombinant DNA technology has been more focused on producing species which are specific to the certain enzyme production by manipulating and directing their genes. Below are the lists of the Industrial enzymes used in Dairy Industry popular in the 21st century Enzyme market:
Enzyme | Function | Microorganisms |
| Acid proteinase | Milk coagulation | Aspergillus sp. |
| Neutral proteinase | Faster cheese ripening, debittering | Bacillus subtilis, A. oryzae |
| Lipase | Faster cheese ripening, flavor customized cheese, | Aspergillus niger, A. oryzae |
| Lactase (β-galactosidase) | Lactose reduced milk and whey products | A. niger, Escherichia coli, Kluyveromyces sp. |
| Aminopeptidase | Faster cheese ripening, Flavoring and taste improvement | Lactobacillus sp. |
| catalase | Cheese processing | Aspergillus niger |
Acid Proteinase and Neutral Proteinase
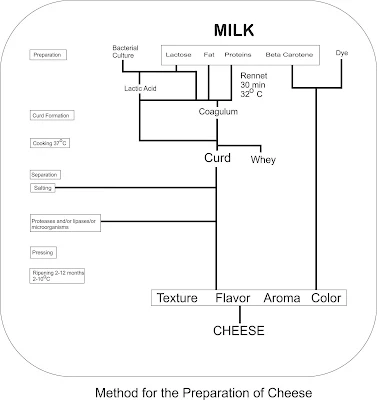
Proteinases are enzymes used in the milk industry to catalyze/hydrolyze the milk protein (casein), which stabilizes micelle formation preventing coagulation. The enzymes are widely used in the dairy industry for cheese processing.
Neutral proteinase refers to a class of proteinases that can act catalysis in a neutral, weakly acidic, or weakly alkaline environment. Its optimal pH is between 6.0 and 7.5, and can catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds of proteins, releasing amino acids or peptides; where as Acid proteinase refers to class of proteinases that can act in acidic environment, helping in milk coagulation.
Lipase
Lipases are the enzymes which are naturally found in our small intestine which digests the fats and lipids. This enzyme finds application in various industries including food, biofuel, detergents and animal feed. It is also used in leather, textile and paper processing applications. In the food and beverage industry, lipases find major application in dairy, baking, fruit juice, beer and wine industries.
Commercial lipases are mainly used for flavor development in dairy products and processing of other foods containing fat. They can improve the characteristic flavor of cheese by acting on the milk fats to produce free fatty acids after hydrolysis. Different types of cheese can be made by using lipases from various sources, e.g. Romano cheese using kid/lamb pre-gastric lipase, Camembert cheese using lipase from Penicillium camemberti and cheddar cheese using Aspergillus niger or A. oryzae. Lipase catalysis could improve the texture and softness of cheese. Lipases are also used as flavor development agents in butter and margarine, also to prolong the shelf life of various baking products.
Lactase Enzyme
It is popularly known as Lactase (beta galactosidase are enzymes classified as hydrolases). The enzyme digest the lactose found in milk into glucose and galactose. Because of intestinal enzyme insufficiency, some individuals even a population, show lactose intolerance and difficulty in consuming milk and dairy products. Hence, low-lactose or lactose-free food aid programme is essential for lactose intolerant people to prevent severe tissue dehydration, diarrhea, and at times, even death.
Another advantage of lactase-treated (to produce lactose free milk) milk is the increased sweetness of the resultant milk, thereby avoiding the requirement for addition of sugars in the manufacture of flavored milk drinks. Manufacturers of ice cream, yoghurt and frozen desserts use lactase to improve scoop and creaminess, sweetness, and digestibility and to reduce sandiness due to crystallization of lactose in concentrated preparations. Also Cheese manufactured from hydrolyzed milk ripens more quickly than the cheese manufactured from normal milk.
A. niger, Escherichia coli, Kluyveromyces sp. not only produces various enzymes but it is one of the few species classified as GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). A. niger is used in the production of enzymes, its cell mass is used as a component in animal feed and its fermentation produces organic acids and other compounds of high economic value.
Amino Peptidase
The proteolytic system of lactic acid bacteria contribute to the development of flavor during the ripening of cheese through the generation of short peptides and free amino acids, which directly or indirectly act as flavor precursors. Newly isolated lactic acid bacteria (LAB) as well as those procured from culture collection centers were screened for the production of various substrate specific amino peptidases. Peptidases are the enzymes used to break the bitter peptides found in the cheese and milk during processing to enhance the flavor and taste, Also it is used in faster cheese ripening.
Catalase
Catalase is an enzyme found in all living organisms exposed to oxygen. It is mainly a tetrameric protein found in the aerobic organisms. It catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It helps the cell from protecting themselves from oxidative damage from reactive oxygen species. Catalase is used in food and dairy industry for the food preservation. Catalase is applied in milk processing industry to eliminate peroxide from milk, to remove glucose from egg white in baking industry and in food wrappers to prevent oxidation and control perishability of food. This enzyme has limited use in cheese production (Removal of hydrogen peroxide from milk prior to cheese production).